Characteristics of a new generation of ceramic foam filter materials
Characteristics of a new generation of ceramic foam filter materials
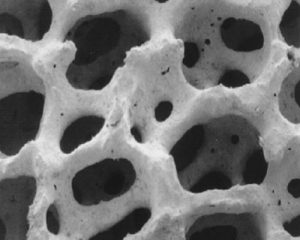
In order to achieve the research and development goals we determined, a complete set of strict manufacturing technology has been studied from material selection, pulping and mixing, carrier pretreatment, infrared drying, sputter coating, and microwave drying, to temperature field control of roasting. The new generation of ceramic foam filter materials developed by AdTech can effectively improve the cleanliness of aluminum melt.
The characteristics of our company's new generation of ceramic foam filter materials
| The second generation of ceramic foam filter plate (three-dimensional network) | The first generation of ceramic foam filter plate | |
| Material | Xpert Pro-MPD diffractometer analysis Main crystal phase: alpha alumina, polymorphic mullite, no quartz glass phase | Xpert Pro-MPD diffractometer analysis of the main crystal phase: cordierite or mullite or with spinel phase, and quartz glass phase |
| Mesh structure | The three-dimensional network has a uniform bone structure, and the skeleton branches have microscopic cracks and microscopic pinholes; the thermal shock resistance is strong and the ceramsite is not lost; the microscopic defects are conducive to the secondary deposition of fluoride and increase the adsorption capacity of the impurity phase in the aluminum liquid. | The uneven bone structure of the three-dimensional network, especially in the transverse direction of the longitudinal section, has blind holes and is honeycomb-shaped; the skeleton branches are smooth or there are many broken cracks, and the ceramsite is easily dropped by vibration; the filtration is completely intercepted by mechanical collision. |
| Phenomenon | The compressive strength is greater than 4.5 N/mm2, the bending strength is 1.5 N/mm2, and the thermal shock resistance (750 degrees Celsius) is greater than 5 times without ceramsite; The static pressure difference varies greatly. | The compressive strength is less than 4 N/mm2, generally (1.0-1.5) N/mm2; the thermal shock resistance is less. |
| Exterior | Pink or clean white; no ceramsite is lost when beaten. | White or off-white; the ceramsite will fall off when it is beaten, and the more ceramsite is shaken, the more ceramsite will be removed. |
| Misunderstanding | Adsorption filtration has a high impurity removal rate, and sometimes the static pressure difference increases sharply due to too many filtration impurities, resulting in insufficient flow and blockage. | Due to a large number of blind holes in the middle cross-section, the effective filtration volume decreases, causing insufficient flow or even blockage. |
The mechanism of ceramic foam filter plate filtering and purifying aluminum melt The mechanism of ceramic foam filter plate filtering and purifying aluminum melt is generally described as diffusion interception and inertial collision interception or screening mechanism, sedimentary layer, and deep bed filter mechanism. The State Key Laboratory of Tsinghua University has established a three-dimensional physical model and a two-phase flow model for the filtration mechanism of ceramic foam filters and carried out simulation calculations, which are very helpful for our research on the filtration and purification of molten aluminum. The process of filtration and purification of molten aluminum by ceramic foam filter plate is very complicated, which is a complex process of high-temperature physical chemistry and metallurgical dynamics.
As for screening, collision, sedimentation, interception, and filtration, it is relatively easy to understand. We have conducted a comprehensive analysis of many parameters obtained during the research process of aluminum melt filtration with ceramic foam filter plates and put forward the following insights:




